The Power of Caching: Boosting API Performance and Scalability
DZone
AUGUST 16, 2023
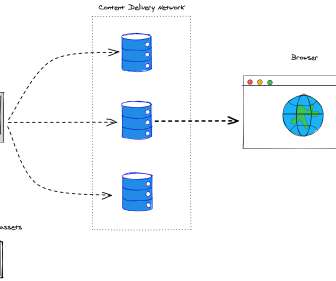
Caching is the process of storing frequently accessed data or resources in a temporary storage location, such as memory or disk, to improve retrieval speed and reduce the need for repetitive processing. Bandwidth optimization: Caching reduces the amount of data transferred over the network, minimizing bandwidth usage and improving efficiency.









































Let's personalize your content