AI-powered DNS request tracking extends infrastructure observability for high quality network traffic
Dynatrace
OCTOBER 1, 2020
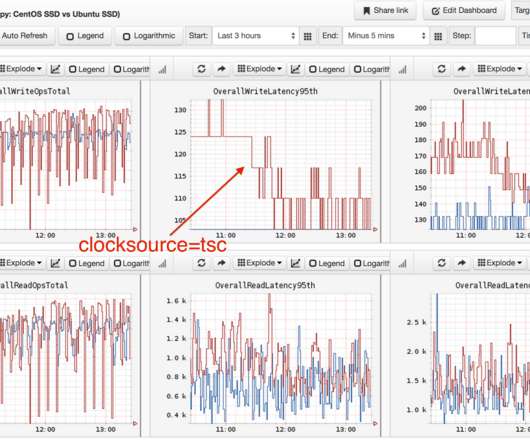
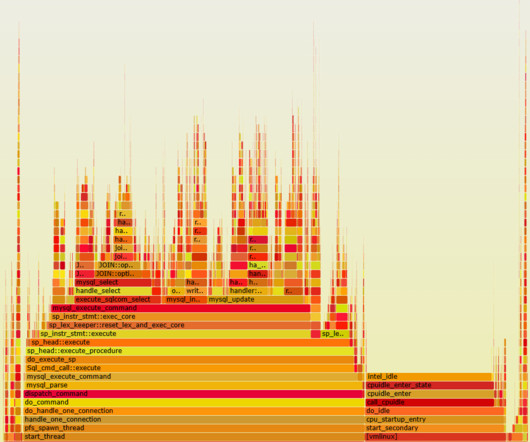
Applications and services are often slowed down by under-performing DNS communications or misconfigured DNS servers, which can result in frustrated customers uninstalling your application. While our competitors only provide generic traffic monitoring without artificial intelligence, Dynatrace automatically analyzes DNS-related anomalies.









































Let's personalize your content