Seeing through hardware counters: a journey to threefold performance increase
The Netflix TechBlog
NOVEMBER 9, 2022
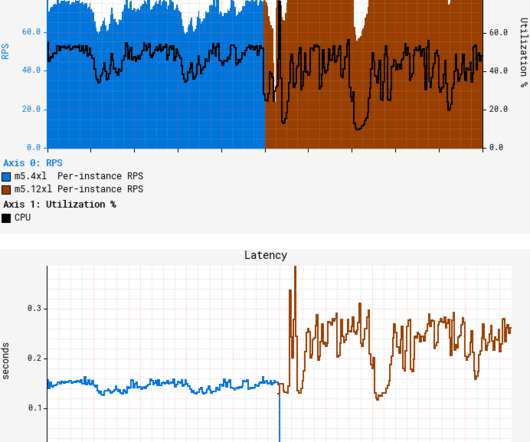
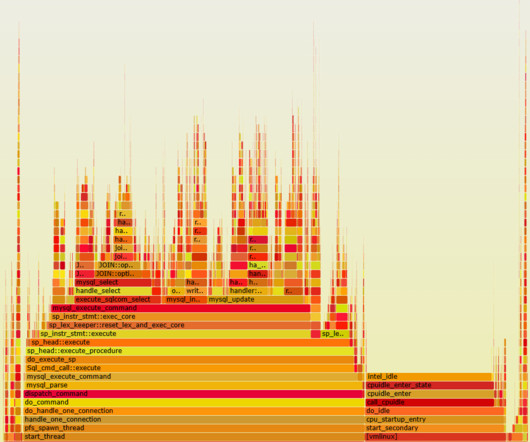
A quick canary test was free of errors and showed lower latency, which is expected given that our standard canary setup routes an equal amount of traffic to both the baseline running on 4xl and the canary on 12xl. Thread 0’s cache in this example. Resolving coherency across private caches takes time and causes CPU stalls.






































Let's personalize your content