Dynatrace Managed turnkey Premium High Availability for globally distributed data centers (Early Adopter)
Dynatrace
JUNE 25, 2020
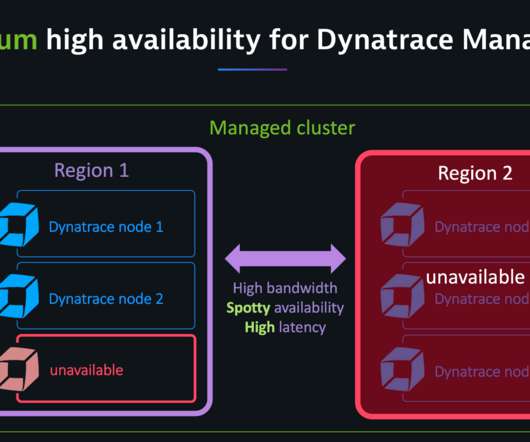
Our Premium High Availability comes with the following features: Active-active deployment model for optimum hardware utilization. Minimized cross-data center network traffic. Save on costs for hardware and network bandwidth to optimize total cost of ownership. Automatic recovery for outages for up to 72 hours. How it works.




















Let's personalize your content