Use Distributed Caching to Accelerate Online Web Sites
ScaleOut Software
APRIL 22, 2020
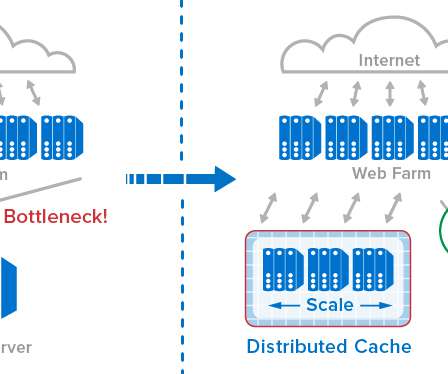
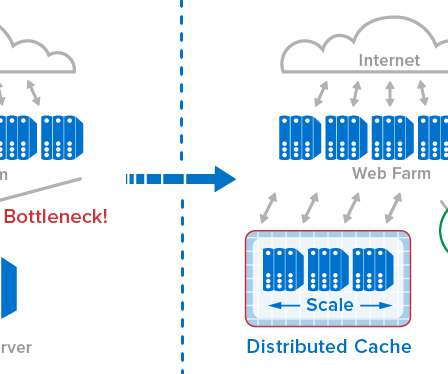
The Solution: Distributed Caching. A widely used technology called distributed caching meets this need by storing frequently accessed data in memory on a server farm instead of within a database. It’s not enough simply to lash together a set of servers hosting a collection of in-memory caches.













Let's personalize your content