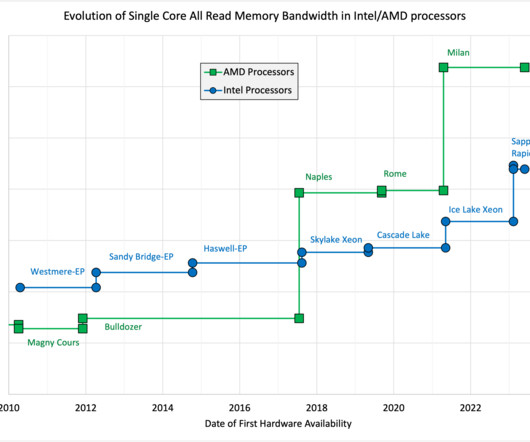
The evolution of single-core bandwidth in multicore processors
John McCalpin
APRIL 25, 2023
For most high-end processors these values have remained in the range of 75% to 85% of the peak DRAM bandwidth of the system over the past 15-20 years — an amazing accomplishment given the increase in core count (with its associated cache coherence issues), number of DRAM channels, and ever-increasing pipelining of the DRAMs themselves.








Let's personalize your content