The Amazing Evolution of In-Memory Computing
ScaleOut Software
JUNE 22, 2020
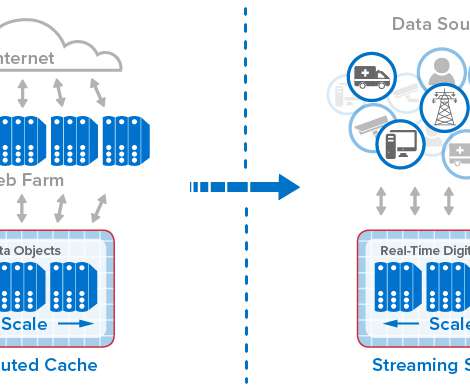
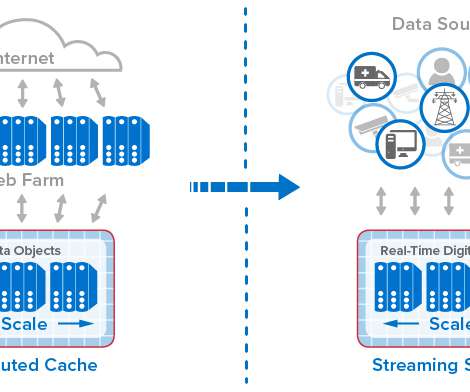
In general terms, in-memory computing refers to the related concepts of (a) storing fast-changing data in primary memory instead of in secondary storage and (b) employing scalable computing techniques to distribute a workload across a cluster of servers.













Let's personalize your content