Observability platform vs. observability tools
Dynatrace
DECEMBER 22, 2021
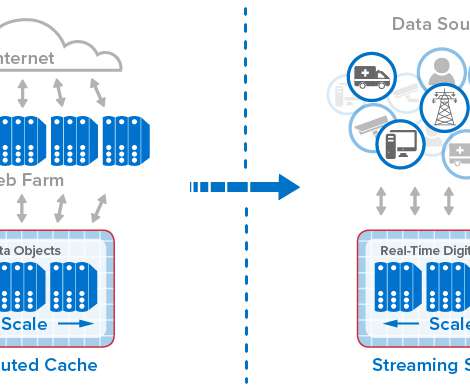
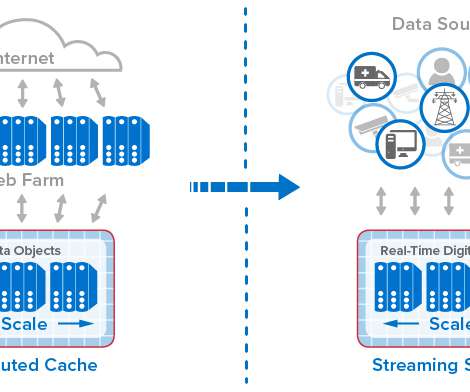
Complex information systems fail in unexpected ways. Observability gives developers and system operators real-time awareness of a highly distributed system’s current state based on the data it generates. With observability, teams can understand what part of a system is performing poorly and how to correct the problem.













Let's personalize your content