Today’s organizations flock to multicloud environments for myriad reasons, including increased scalability, agility, and performance. However, these environments can drown enterprises in data, forcing them to adopt multiple tools and services to manage and secure it. This fragmented approach adds complexity and opens the door to security vulnerabilities.
In fact, according to recent Dynatrace research, 85% of technology leaders say the number of tools, platforms, dashboards, and applications they use adds to the complexity of managing a multicloud environment. Further, 84% of technology leaders say multicloud complexity makes it harder to protect applications from security vulnerabilities and attacks.
With unified observability and security, organizations can protect their data and avoid tool sprawl with a single platform that delivers AI-driven analytics and intelligent automation.
During a Dynatrace Perform 2024 breakout session, Dynatrace colleagues Bipin Singh, product marketing director, and Markie Duby, principal solutions engineer, showed how organizations can bring together observability, security, and business data from cloud-native and multicloud environments with Dynatrace.
The secret sauce of unified observability
Observability enables teams to measure a system’s state based on the data it generates. A unified observability approach takes it a step further, enabling teams to monitor and secure their full stack on an AI-powered data platform.
With the Davis AI engine, Grail data lakehouse, and Smartscape topology visualization at its core, the Dynatrace unified observability and security platform provides AI-driven analytics and automation capabilities.
“Grail handles data storage, data management, and processes data at massive speed, scale, and cost efficiency,” Singh said. “Smartscape contextualizes your entire environment and builds a real-time topology map that’s dynamic and stays up to date as your environment changes. And the Davis AI engine is continuously watching your environment and evaluating the emerging situation, automatically detecting problems, creating automated root-cause analysis for you and business impact analysis for prioritization.”
The importance of hypermodal AI to unified observability
Artificial intelligence is a critical aspect of a unified observability strategy. In fact, according to the recent Dynatrace report, “The state of AI 2024,” 83% of technology leaders say AI has become mandatory to keep up with the growing complexity of multicloud environments.
The Davis AI engine uses a hypermodal approach to bring together causal, predictive, and generative AI. Causal AI determines the underlying causes and effects of issues based on the system’s topology. Predictive AI, meanwhile, makes predictions about future events based on patterns from historical data. And generative AI, termed Davis CoPilot, creates queries, notebooks, and dashboards to simplify analytics, and provides workflow and automation recommendations.
By bringing together these AI types, organizations receive generative AI recommendations based on the precise context from predictive and causal AI. This coactive AI approach enables organizations to spend more time on innovation by simplifying and automating routine tasks.
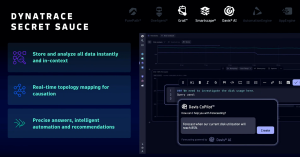
How Davis tackles root cause for AI-driven analytics
Duby discussed how Dynatrace OneAgent, Smartscape, and Davis work together to take information from many different layers in a full stack to provide root-cause analysis.
“When [Davis is] going through and detecting anomalies within your environment, it’s using data both from the underlying interdependency link as well as that end-to-end trace from the end user all the way back in order to do things like root-cause analysis,” Duby said. “We’re using that causal AI to determine what is actually the underlying root cause.”
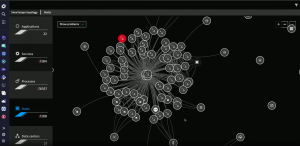
Davis enables users to go deeper into the details of the underlying processes running on a particular host. The hypermodal AI engine shows what’s happening in a system down to the data coming in, while presenting the information in context.
“It’s one thing to have the data; it’s another thing to have it in context,” Duby continued. “For performance, for security analytics, you have to have the data in context. You need to understand how these different pieces interact with each other and how those pieces are actually coming through.”
Once Davis has gathered all the necessary information throughout the different layers of the stack, it can determine what’s changing, what’s breaking, where the issues are, and how to resolve them. Additionally, it helps users prioritize which issues need immediate attention by providing the necessary context.
“[Davis is] looking at the business context—not just the IT, not just the individual metrics, but understanding the whole picture,” Duby said.
How Davis CoPilot takes AI further and promotes collaboration
A significant piece of the Dynatrace hypermodal AI approach is Davis CoPilot, the generative AI part of the hypermodal engine. Davis CoPilot enables users to create queries, dashboards, and notebooks using natural language input, while offering coding suggestions for workflow automation. Additionally, it simplifies the processes of onboarding, configuring, and adopting the Dynatrace unified observability and security platform.
“This is Davis CoPilot. This is your helper to make sure you can actually go in and take advantage of all of that underlying data,” Duby said. “So, you have the analytics and the performance tracking that Dynatrace is doing, and you also have the ability to build it for your own custom use case.”
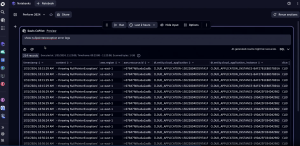
In addition to creating queries, dashboards, and notebooks using natural language, Davis CoPilot enables users to share these notebooks with other team members across the organization, boosting collaboration efforts.
“[Davis CoPilot will] start building out queries. And now I can take this information that I just got back, and I can share this notebook with my colleague. And now they have the exact same information,” Duby continued. “I can reuse the same report next month and see if it changed. … This functionality allows me to collaborate with my team. It allows me to run with a new idea and see what comes back. And then I can take this information, and I can build on top of it to do more advanced analytics for my different teams.”
For an in-depth demonstration of using the Dynatrace unified observability and security platform, watch our on-demand session, “AI-driven analytics and automation for unified observability and security.” And for more coverage from Perform 2024, check out our guide.



Looking for answers?
Start a new discussion or ask for help in our Q&A forum.
Go to forum