Data synchronization in SQL Server Always On Availability Groups
SQL Shack
MAY 3, 2019
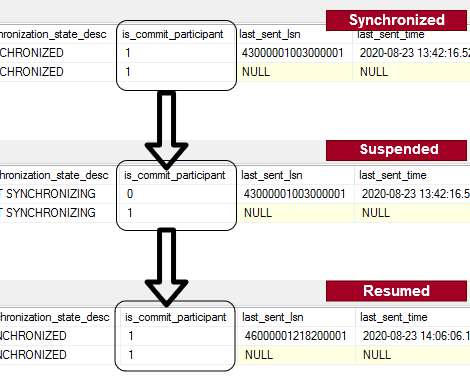
This article describes the data synchronization process on SQL Server Always On Availability Groups in both Synchronous, and Asynchronous data commit mode. High data availability is an important aspect of every DBA’s life.
















Let's personalize your content