What is a Distributed Storage System
Scalegrid
FEBRUARY 8, 2024
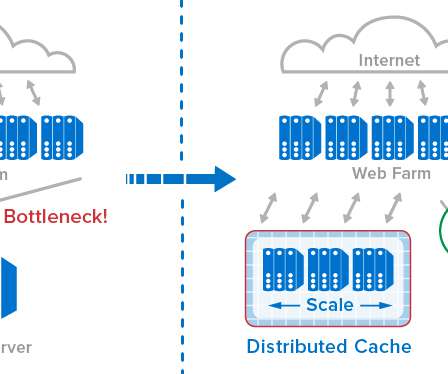
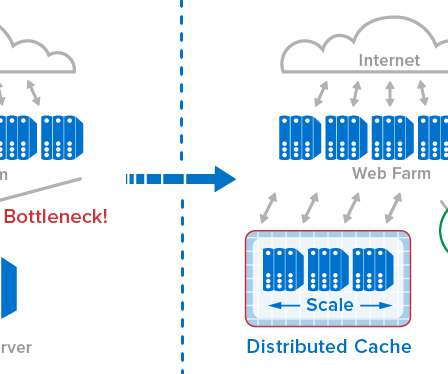
Key Takeaways Distributed storage systems benefit organizations by enhancing data availability, fault tolerance, and system scalability, leading to cost savings from reduced hardware needs, energy consumption, and personnel. This strategy reduces the volume needed during retrieval operations.
































Let's personalize your content